About Me
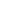
In today's digital age, the collection and management of personal information have become integral to various business operations. This section delves into the multifaceted world of information aggregator solutions, examining how these platforms facilitate the exchange of data among entities. While they offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and accessibility, they also raise critical questions about privacy and ethical considerations.
Information aggregators play a pivotal role in connecting businesses with the data they need to make informed decisions. These platforms compile vast amounts of personal details from diverse sources, enabling companies to target their marketing efforts more effectively and tailor their services to individual preferences. However, this convenience comes with a caveat. The extensive gathering and dissemination of personal information can lead to privacy breaches and misuse, highlighting the need for stringent regulations and ethical practices.
Moreover, the reliance on information aggregators can sometimes overshadow the potential for data inaccuracies and biases. While these platforms promise comprehensive and up-to-date information, the reality can be quite different. Inconsistencies in data collection methods and the potential for outdated information can undermine the reliability of insights derived from these sources. This raises important questions about the integrity of the data and the potential consequences for businesses and consumers alike.
In conclusion, while information aggregator solutions offer numerous benefits in terms of data availability and business intelligence, they also present significant challenges. Balancing the need for efficient data management with the imperative to protect individual privacy and ensure data accuracy is a complex task. As we navigate this landscape, it is crucial to foster a dialogue that addresses both the opportunities and the risks associated with these powerful tools.
Understanding Information Aggregator Mechanisms
This section delves into the intricate aspects of privacy that arise when individuals' information is collected and managed by third-party entities. It explores how these entities handle sensitive personal data and the implications for users' privacy.
Information aggregators, often referred to in simpler terms, gather vast amounts of personal details from various sources. This collection process can include data from public records, online activities, and even private transactions. The following table outlines some key concerns related to privacy that users should be aware of when dealing with these entities.
| Aspect | Concern | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Excessive gathering of personal information | Increased risk of identity theft and unauthorized use |
| Data Usage | Lack of clarity on how information is utilized | Potential for misuse in marketing or other commercial activities |
| Data Security | Inadequate protection measures | High vulnerability to cyber-attacks and data breaches |
| User Control | Limited ability for individuals to manage or delete their data | Loss of personal data autonomy and privacy |
Addressing these privacy concerns is crucial not only for safeguarding individual rights but also for fostering trust in the digital economy. It is essential for users to understand their rights and for information aggregators to adopt transparent and secure practices.
Privacy Concerns with Data Brokers

This section delves into the intricate issues surrounding the confidentiality and security of personal information managed by intermediaries. As these entities aggregate and distribute vast amounts of sensitive data, the potential risks to individual privacy are significant.
One of the primary concerns is the lack of transparency in how these intermediaries collect, process, and share personal information. Consumers often have little to no knowledge about the extent of their data being collected or the purposes for which it is used. This lack of awareness can lead to unauthorized data usage and potential breaches.
| Aspect | Concern | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Over-collection of personal information | Increased risk of data breaches |
| Data Usage | Unauthorized usage for marketing or other purposes | Invasion of privacy |
| Data Sharing | Lack of control over data distribution | Potential misuse by third parties |
Furthermore, the integration of personal data across various platforms and services can amplify privacy risks. Without stringent regulations and oversight, there is a significant threat of data being misused, leading to financial, reputational, and emotional harm to individuals.
Addressing these concerns requires a comprehensive approach, including stronger regulatory frameworks, increased transparency from intermediaries, and greater consumer empowerment in managing their personal data.
Benefits of Data Broker Accuracy
This section delves into the advantages that stem from the precise collection and management of information by intermediaries. High accuracy in the handling of personal details not only enhances the reliability of the information but also contributes to more effective decision-making processes across various sectors.
Accurate information management by these intermediaries significantly impacts the efficiency of operations in industries such as marketing, finance, and healthcare. It ensures that the information utilized for strategic planning is both relevant and up-to-date, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors and enhancing the overall quality of services provided.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Decision Making | Accurate information allows for more informed decisions, leading to better outcomes in marketing strategies and financial investments. |
| Increased Efficiency | Precise data management reduces the time and resources required for data verification, thereby increasing operational efficiency. |
| Improved Customer Satisfaction | Accurate targeting based on precise information leads to more relevant offerings, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. |
| Reduced Risk | High accuracy minimizes the risk of legal issues arising from incorrect information, ensuring compliance with regulations. |
Moreover, the economic benefits of accurate information cannot be overstated. It fosters a more transparent and trustworthy marketplace, encouraging investment and economic growth. Businesses that rely on accurate information are better positioned to adapt to market changes and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
In conclusion, the precision of information handled by intermediaries plays a crucial role in the modern economy. It not only supports more effective business practices but also contributes to a more reliable and efficient market environment.
Regulatory Oversight of Data Brokers
This section delves into the mechanisms and entities that monitor and govern the activities of information aggregators. It explores how these regulatory frameworks aim to ensure compliance with privacy laws and protect consumer rights.
The oversight of information aggregators is crucial to maintain ethical standards and legal compliance. Several key areas are addressed by regulatory bodies:
- Compliance with Privacy Laws: Regulatory agencies ensure that information aggregators adhere to local and international privacy regulations, safeguarding personal information from misuse.
- Consumer Protection: These bodies work to protect consumers by enforcing rules that prevent unauthorized data collection and use, ensuring that individuals have control over their personal information.
- Transparency Requirements: Regulatory oversight mandates that information aggregators provide clear and accessible information about their data practices, including how data is collected, used, and shared.
- Enforcement Actions: When violations occur, regulatory agencies have the authority to impose fines and other penalties, ensuring accountability and deterring future breaches.
The effectiveness of these regulatory measures is continually evaluated and adjusted based on technological advancements and emerging privacy concerns. This dynamic approach ensures that the regulatory landscape remains relevant and effective in protecting consumer interests.
Data Broker Transparency Issues
This section delves into the challenges associated with the clarity and openness of information practices within the industry. It explores how these entities collect, use, and share personal information, and the implications of such practices on consumer trust and understanding.
Transparency in this sector is crucial for maintaining public confidence and ensuring ethical conduct. However, several issues hinder the clarity of operations:
- Complexity of Information Handling: Many companies operate with intricate systems that are not easily understandable by the average consumer. This complexity can obscure how personal data is processed and utilized.
- Lack of Clear Communication: There is often a gap in how these companies communicate their practices to consumers. This lack of clear, accessible information can lead to misunderstandings and mistrust.
- Inconsistent Disclosure Practices: Disclosure of data collection and usage varies widely among companies, making it difficult for consumers to know what to expect or how to protect their information.
- Impact on Consumer Rights: The opacity in data handling can undermine consumer rights to know and control how their personal information is used, stored, and shared.
Addressing these transparency issues is essential for the industry to evolve in a manner that respects consumer privacy and fosters trust. Implementing clearer communication strategies, standardizing disclosure practices, and simplifying information handling processes are critical steps towards enhancing transparency.
The Role of Information Aggregators in Marketing

In the contemporary business landscape, information aggregators play a pivotal role in shaping marketing strategies. This section delves into how these entities facilitate targeted advertising and enhance consumer engagement through the collation and analysis of vast amounts of personal information.
Information aggregators collect and analyze consumer data, which is then used by marketers to tailor their advertising efforts. This targeted approach not only increases the effectiveness of marketing campaigns but also improves customer satisfaction by presenting relevant offers. The following table illustrates the typical workflow of information aggregators in the marketing process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Collection | Aggregators gather data from various sources including social media, public records, and online transactions. |
| 2. Analysis | The collected data is analyzed to identify patterns and preferences. |
| 3. Segmentation | Data is segmented into different categories based on demographics, interests, and purchasing behavior. |
| 4. Application | Marketers use this segmented information to create targeted marketing campaigns. |
| 5. Feedback | Results of the campaigns are monitored and analyzed to refine future strategies. |
The integration of information aggregators in marketing not only streamlines the advertising process but also provides valuable insights that can lead to more personalized and effective marketing strategies. However, this practice also raises concerns regarding privacy and the ethical use of personal information, which must be carefully managed to maintain consumer trust.
Security Measures by Data Brokers
In the realm of information management, entities that aggregate and distribute personal details must prioritize robust safeguards to protect sensitive information. This section delves into the various strategies employed by these entities to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data they handle.
Ensuring the safety of collected information is paramount. Here are some key measures implemented:
- Encryption: Sensitive details are encoded to prevent unauthorized access during transmission and storage.
- Access Controls: Strict protocols limit who can view or manipulate the information, often requiring multi-factor authentication.
- Regular Audits: Periodic checks help identify and rectify any vulnerabilities or breaches in security systems.
- Incident Response Plans: Pre-established procedures are in place to swiftly address any security incidents.
- Employee Training: Staff are educated on best practices and the importance of maintaining data confidentiality.
- Physical Security: Measures are taken to protect servers and storage facilities from physical tampering or theft.
- Third-Party Assessments: Independent evaluations by cybersecurity experts ensure that security measures meet industry standards.
By implementing these comprehensive security measures, these entities aim to build trust with consumers and comply with regulatory requirements, thereby safeguarding personal information from potential threats.
Consumer Control Over Data
In the digital age, individuals often find themselves at the mercy of vast information networks that collect and disseminate personal details. This section delves into the mechanisms through which consumers can regain some degree of autonomy over their own information, ensuring that it is used in ways that align with their preferences and expectations.
Understanding Personal Information Rights
Every consumer has inherent rights concerning their personal information. These rights include the ability to access, correct, and delete their data. Recognizing these rights is crucial for individuals to effectively manage their digital footprint.
Tools and Platforms for Data Management
Numerous tools and platforms have emerged to assist consumers in controlling their information. These resources provide interfaces that allow users to view, modify, and remove their personal details from various databases. Such tools empower individuals by offering transparency and control over their digital identities.
Legislation and Policy Influence
Governmental and non-governmental organizations play a significant role in shaping consumer rights regarding personal information. Policies such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe set stringent standards for information handling, giving consumers more power over their data.
Educational Initiatives
Raising awareness about data privacy and control is essential. Educational campaigns help consumers understand the importance of managing their information and how to do so effectively. By enhancing digital literacy, these initiatives contribute to a more informed and proactive consumer base.
Future Outlook
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methods of information collection and usage. It is imperative that consumer control mechanisms keep pace with these advancements. Future developments may include more sophisticated tools for data management and potentially, more robust legislative frameworks to protect consumer rights.
Economic Impact of Data Broker Services

This section delves into how information intermediary platforms influence the broader economic landscape. It explores the dual nature of their contributions, highlighting both positive advancements and potential drawbacks.
Information intermediary platforms have significantly reshaped various sectors, enhancing efficiency and decision-making processes. Here are some key areas where their impact is notably felt:
- Market Research: These platforms provide invaluable insights that help businesses tailor their strategies to consumer needs, thereby boosting market competitiveness.
- Advertising: By targeting specific demographics, these platforms enable more effective advertising campaigns, leading to higher conversion rates and revenue for businesses.
- Innovation: Access to detailed consumer data fosters innovation, as companies can develop products and services that more accurately meet market demands.
However, the economic benefits are not without challenges. Concerns about privacy and data security can lead to regulatory hurdles, potentially restricting the growth and profitability of these platforms. Additionally, the concentration of market power in the hands of a few major players can stifle competition and innovation.
Looking ahead, the future of information intermediary platforms will likely be shaped by technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations. Key trends to watch include:
- Enhanced Data Privacy Measures: As privacy concerns grow, platforms will need to adopt more robust data protection measures to maintain consumer trust and comply with regulations.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: These technologies will enable more sophisticated data analysis, offering deeper insights and more personalized marketing strategies.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: As global connectivity increases, these platforms will expand their reach into new markets, driving economic growth in these regions.
In conclusion, while information intermediary platforms offer substantial economic benefits, their future success will depend on balancing innovation with ethical considerations and regulatory compliance.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage
Exploring the evolving landscape of information intermediation, this section delves into the anticipated developments within the sector that facilitates the exchange of personal details. As technology advances and regulatory frameworks adapt, the industry is poised for significant transformations that could redefine how sensitive information is managed and utilized.
One of the foremost trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. These tools are expected to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of information processing, enabling more sophisticated analysis and prediction models. This could lead to more targeted and effective marketing strategies, but also raises concerns about the ethical implications of AI in handling personal details.
Another trend is the increasing emphasis on privacy protection and compliance with stringent regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Companies are likely to invest more in robust security protocols and transparent practices to ensure they meet these regulatory standards. This shift could also drive innovations in anonymization techniques and secure data storage solutions.
The rise of blockchain technology is another significant development. Blockchain offers a decentralized and immutable ledger, which could revolutionize the way transactions involving personal information are recorded and verified. This technology could enhance transparency and trust in the industry, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Additionally, there is a growing trend towards consumer empowerment. As awareness about personal data rights increases, consumers are likely to demand more control over their information. This could lead to the development of more user-friendly tools and platforms that allow individuals to manage their data profiles actively, including the ability to Opt-out BlockShopper guide or modify shared details.
Lastly, the economic impact of these trends cannot be overlooked. The evolving landscape could reshape the competitive dynamics within the industry, influencing pricing models, service offerings, and overall market strategies. Companies that successfully navigate these changes will be well-positioned to capitalize on new opportunities and meet the evolving needs of consumers and businesses alike.
Location
Occupation